By Deneece Ferrales
Feb. 7 is National Black HIV/AIDS Awareness Day. Uriah Robertson and the team at Waco-McLennan Public Health District who work in the clinic for HIV/AIDS services are preparing to use the occasion to raise HIV/AIDS awareness and encourage testing.“

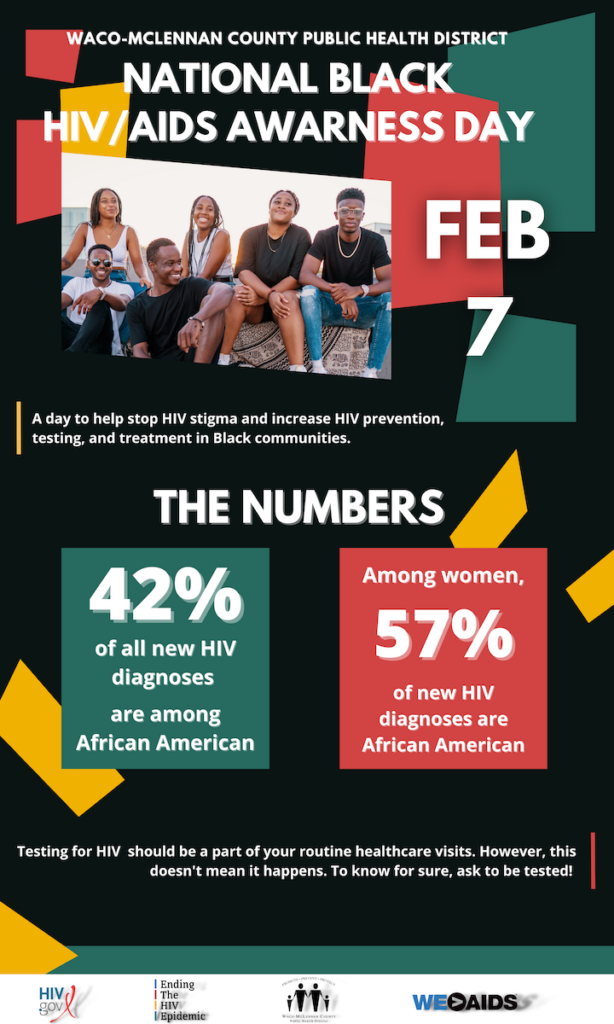
Studies show that African Americans make up about 45 or 47 percent of new HIV diagnoses,” Robertson said. “Amongst women, we are seeing that African American women are 57 percent of new diagnoses. So, how do we decrease the numbers? We have to educate, advocate, encourage routine testing and so much more.”
As a risk reduction specialist, Robertson said his job is to “work with the community to provide intervention and prevention tools. We even perform HIV testing and encourage the importance of knowing your status.” Risk reduction specialists “have those conversations that others are afraid to have. We work to build rapport with our clients so we can get out into the clinic so that we can get the word out about our services while also working to break down the walls of stigma about HIV/AIDS.”
According to HIV.gov, a website managed by the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, he first Black HIV/AIDS Awareness Day was held in 1999 as a grassroots opportunity to raise awareness in minority communities. In 2001, the day was given national status. This became needed as the number of new infections were disproportionately affecting people of color, particularly Black communities. At that point, new cases of HIV were escalating so quickly in the Black community that national leaders and the Centers for Disease Control began concerted efforts to combat the spread of HIV/AIDS in communities of color. According to the CDC, the history of these efforts includes:
- In 1998, the Congressional Black Caucus joined African American leaders from all over the U.S. to declare a “state of emergency” and created the Minority AIDS Initiative to offer funding for prevention efforts in Black communities. The CDC launched an array of prevention efforts aimed at preventing the spread of HIV among African Americans as a result of this funding.
- In 2000, HIV cases among Black and Latino men exceeded cases among White men, which was disproportionate to the general population, thus calling attention to health inequities surrounding the spread of HIV/AIDS.
- In 2007, the CDC launched its expanded HIV testing initiative to increase testing opportunities, primarily among African Americans.
- In 2008, the Black AIDS Institute reported that if Black America were its own country, it would rank 16th in the world in terms of number of people with HIV. It was estimated that 1 in 16 Black men would contract HIV/AIDS in their lifetime (approximately 6% of the population) and 1 in 32 Black women would contract HIV/AIDS in their lifetime.
- In 2010, the Obama Administration released first National HIV/AIDS strategy for the United States, which called on the nation to focus HIV prevention efforts on those at greatest risk, including African Americans.
Despite these efforts, sadly, this has not changed in the past 23 years. African Americans, more than any other race, have the highest rates of HIV infection in the nation. Black Americans account for approximately 14% of the U.S. population, but nearly half of those living and dying with HIV and AIDS are Black. Within this population, gay and bisexual men are the most affected, followed by heterosexual women. AIDS is the third leading cause of death among Black women aged 25–34 and 35– 44 and among Black men aged 35–44 (CDC).
Not only does this health inequity appear in the number of African Americans contracting HIV/AIDS, it also appears in the treatment of HIV/AIDS. Compared to all other persons with HIV, African Americans had the lowest rates of viral suppression. According to the CDC, out of every 100 Black persons living with HIV, only 63 are receiving some type of HIV care, 48 of 100 were retained in HIV care, and 51 of 100 were virally suppressed. This means that little more than half of all African Americans living with HIV received any type of treatment.
Though HIV is preventable, prevention remains the biggest challenge and further calls attention to the health inequities around this disease in Black communities. The challenges to prevention efforts include the stigma of a positive HIV status, people not having awareness of their HIV status, homophobia, racism, and mistrust of the healthcare system.
Lack of awareness of one’s HIV status can also lead to poor HIV treatment outcomes. Further, STI rates among African Americans are higher than among any other minority group, and there is a link between being diagnosed with other Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs) and contracting HIV.
Lastly, persons experiencing poverty, which is higher in Black communities, are less likely to have access to quality healthcare for HIV, stable housing, and HIV prevention services.
So where do we start in addressing this health inequity? The most important place to begin is to encourage testing. If HIV is left untreated, chronic illness and death are the likely outcomes.
The first step to preventing this is for a person to know his or her status. Knowing one’s status can also prevent the further spread of HIV. Health professionals must continue to partner with Black community leaders to make outreach efforts aimed at more testing and increased awareness of prevention.
HIV treatment and prevention has come a long way in the past three decades. On Feb. 7, it is important to increase awareness of the continued need to address HIV prevention and treatment, particularly in Black communities. This is also a great day to encourage testing and the importance of knowing your status. Together, we can continue that fight to eradicate HIV/AIDS.

Deneece Ferrales, Ph.D., is director of health initiatives for Prosper Waco.
The Act Locally Waco blog publishes posts with a connection to these aspirations for Waco. If you are interested in writing for the Act Locally Waco Blog, please email the ALW team — [email protected].
By Deneece Ferrales
For many of us, the new year means time to set our new year’s resolution(s) — a goal or set of goals that are generally designed to help one become happier, healthier, more successful, and/or have increased life enjoyment. According to several studies, health goals are the most common resolutions.

In the United States, exercising more, losing weight, and better mental health are among the top five resolutions every year. These are important, especially in light of the COVID pandemic continuing to limit our contact with others and limiting how and when we can participate in healthy activities such as exercise or even the ability to access healthy foods.
Keeping up a healthy exercise routine and healthy eating are imperative both to our physical and our mental health. Unfortunately, despite our best intentions, many of our resolutions will be abandoned before January ends.
The collective wisdom regarding resolutions has always been that discipline is key and that if we fail at keeping a resolution, it is because of poor self-discipline. However, simply telling ourselves to do it does not lead to success. According to US News & World Reports, we normally set resolutions based on our Christmas excesses (eating, failing to get exercise during the holidays, etc.) without preparing ourselves for the changes we plan to make in our lives.
There is a discomfort that comes with change, even when that change leads to feeling better. We have to readjust our schedules for exercise, amend our shopping habits to seek out healthier foods, or make other intentional changes to our daily routines and habits. This is stressful because the act of change, any change, produces emotional friction.
If we have not determined when and how we plan to exercise or made a plan for any grocery shopping changes needed to be able to purchase healthier foods, then we are doomed to fail when we experience that transient discomfort. It is important to plan for the change and give yourself a step-by-step guide to when and how each change will occur. Even with the best plans, transient discomfort will occur, but it is much easier to follow a well-thought-out plan through the change than to add further stress from indecision.
Here are some tips for keeping those healthy new year’s resolutions:
- Turn your broad health resolutions into specific goals with steps for accomplishing those goals. I like using SMART goals (specific, measurable, attainable, realistic, and timed). SMART helps us think out exactly how and when we plan to make our changes and then gives us time limits for accomplishing our goals. So instead of having a resolution that says, “Get more exercise,” your resolution reads, “Take a mile-long walk 4 times a week for the next three months.”
- Think small. Set your goals for something accomplishable. You may want to run in next year’s marathon, but you have not begun to train yet. Setting a goal that is not reachable or that will require work over a long period of time is likely to lead to disappointing results and goal abandonment. It might be better to start with a smaller goal, like running a mile or running 3 times a week, and as you reach each goal, set another until you are ready to run that marathon.
- Consider your why. Setting goals that lead to better health is always a good idea. The meaning of those goals is different for each person. One person may be diabetic and interested in lowering their A1C, while another person may want to increase stamina to be able to participate in more activities. Whatever your reason, this can be what keeps you motivated on those days when you are not feeling it. If your goals revolve around exercise and/or healthier eating, try to stay away from an appearance-focused why.
- Keep it all in the family! Parents have to consider their children’s needs, which are sometimes unpredictable. Setting a health resolution for the whole family makes reaching your goals a “family affair” and prevents you from having to choose between your family and your own personal growth.
The Robert Wood Johnson Foundation published a report titled, “State of Childhood Obesity: Prioritizing Children’s Health During the Pandemic.” The report states that more than 15% of children (1 in 7) between the ages of 10 and 17 are obese. Childhood obesity leads to a host of health problems in adulthood. For this reason, including the children in developing healthy goals now will give them a foundation for continuing healthy practices.
If setting a family health resolution, call a family meeting so everyone has input. Define what a resolution is so that the entire family understands the importance of setting the goal. Talk about your family’s good health habits and bad ones to determine the best family resolution.
- Write down your goals/resolutions. Writing down your resolutions helps make your goals more intentional. Looking back at the goals can help motivate you and remind you how far you have come toward achieving your goals.
- Share your resolution with others. Telling other people about your goals can help hold you accountable. It can also help you find others who are working on similar goals so that you can achieve them together. Find someone else who wants to exercise and schedule walks or grocery shop together.
- Use technology to your advantage. There are a myriad of apps for your phone that can support you in your quest to meet your goals.
- Look at your goals frequently and review your progress. There are a number of free goal tracking apps that can assist you with this.
- It’s not over just because you veer off course. We all veer off course sometimes. Maybe you had a bad week and weren’t able to walk or you were not able to shop at your regular grocery store and thus had to buy more pre-packaged and less healthy foods. It’s okay. Look back and celebrate the progress you have made and how far you have come then readjust so that you are able to continue moving forward despite the disruption.
Let’s make 2022 a year of healthier living by learning to plan, set, and achieve our health goals. Have a happy and healthy new year!

Deneece Ferrales, Ph.D., is director of health initiatives with Prosper Waco.
